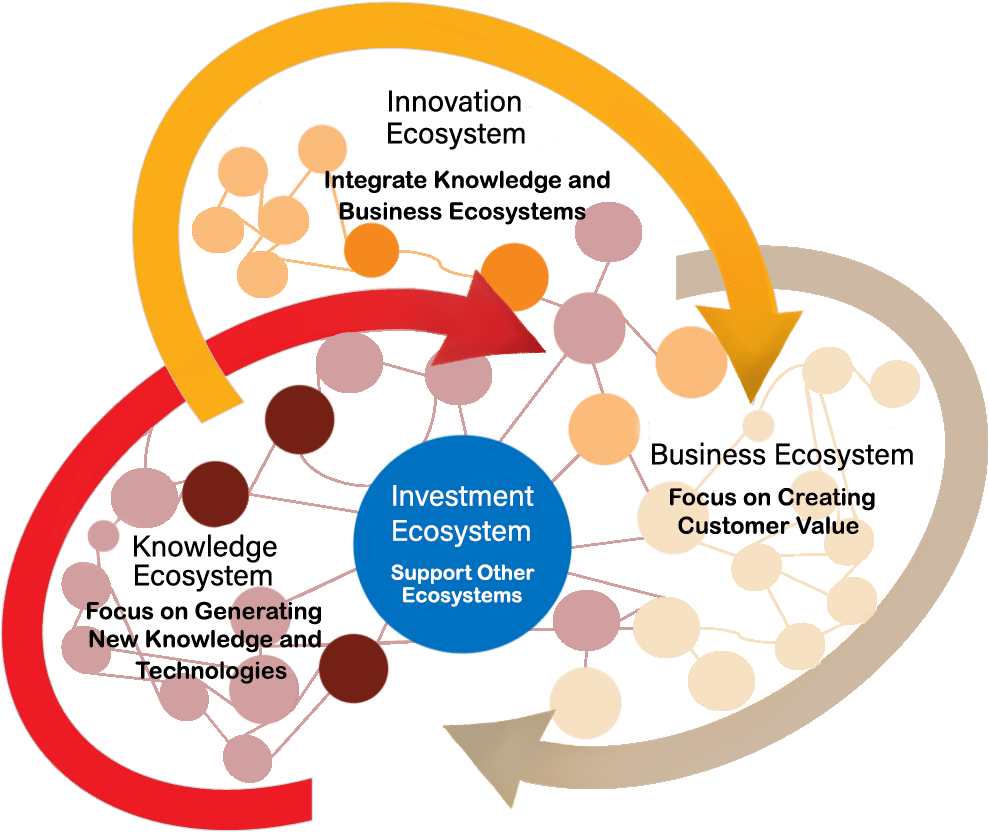
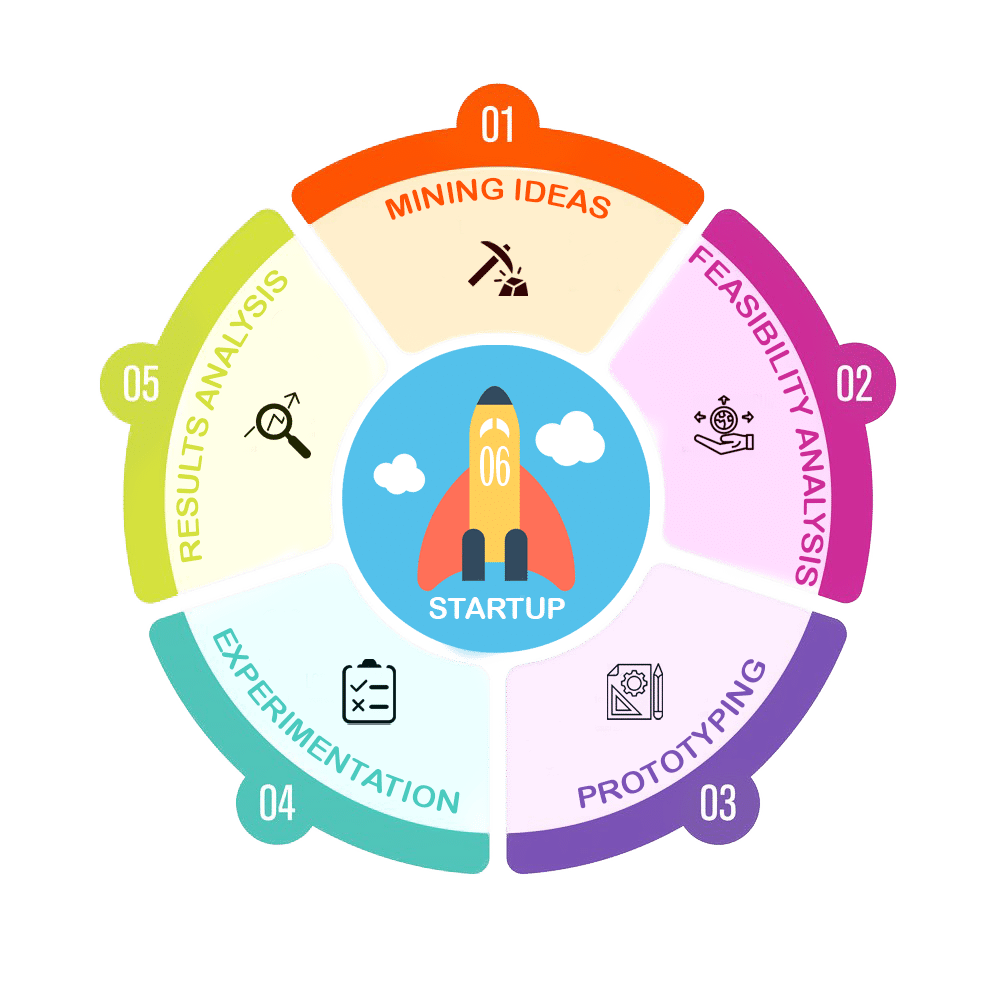
Incubation and Development of Innovative Solutions
At Symplexia, Innovative Solutions come from a systematic and cyclical process that includes from the generation, capture and treatment of new ideas to the final transformation of these ideas into innovative products or services. Through this process, it becomes possible to evaluate the potential of an idea, what adaptations and practical developments need to be made, what costs will be involved, what advantages can be obtained and what return the company will have with the transformation of that idea into a market product .
See Infographic
MINING IDEAS
1 In our internal process of Incubation and Development of Innovative Solutions, the Ideas Mining step is perceived as an operation analogous to the extraction of valuable mineral, such as precious and semi-precious stones. In both cases, the enormous size of some operations, the amount of raw material handled and the waste generated are the major challenge in maintaining an economically sustainable operation.
Read more...1 In our internal process of Incubation and Development of Innovative Solutions, the Ideas Mining step is perceived as an operation analogous to the extraction of valuable mineral, such as precious and semi-precious stones. In both cases, the enormous size of some operations, the amount of raw material handled and the waste generated are the major challenge in maintaining an economically sustainable operation.
The raw material for this stage are Raw Ideas, of any nature, which will be found and collected through a set of tools that includes Corporate Prospecting, Creativity Workshops, Innovation Competitions and Partnerships with Business Incubators and Research Institutions, among others.
The objective of this phase is to build a reasonable stock of raw material (between 500 and 1000 ideas) that will be dealt with in the next step. Before this stock moves on to the next stage, it undergoes preliminary treatment, where similar ideas are grouped, repeated ideas are filtered and documentation is validated.
FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS
2 In this step, the best ideas from the stock are sieved, forming a minimum base (5 to 10 ideas) to be submitted to the prototyping step.
This step requires multidisciplinary knowledge, experience and methodology; thus, right at the beginning, a team of specialists is assembled that will be responsible for conducting this selection.
Read more...2 In this step, the best ideas from the stock are sieved, forming a minimum base (5 to 10 ideas) to be submitted to the prototyping step.
This step requires multidisciplinary knowledge, experience and methodology; thus, right at the beginning, a team of specialists is assembled that will be responsible for conducting this selection.
This team is provided with a set of objectives and clear criteria that define the profile of ideas that we want to find at the end of the selection process.
The selection is made in several screening cycles. In the first cycle, ideas are confronted with the problem or opportunity initially identified, where bad ideas are identified and eliminated very quickly, so that they can no longer drain important resources.
In the second cycle, the remaining ideas are evaluated in terms of originality aspects and the trend of opportunities is verified in relation to the context of the idea.
In the last cycle, it is made the market analysis of the ideas that were selected in the previous sieves and are identified the ideas in which the development of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) are feasible, thus forming the stock of Promising Ideas (“Raw Diamonds”) that will be processed in the next step.


PROTOTYPING
3 In this phase, the Investing Partners define the investment strategy for this Innovation Cycle, providing the budgetary and financial criteria that will allow the choice of “Raw Diamonds” that will initially be cut.
The most promising ideas are analyzed and worked on more deeply, taking into account the costs of developing and prototyping these ideas.
Read more...3 In this phase, the Investing Partners define the investment strategy for this Innovation Cycle, providing the budgetary and financial criteria that will allow the choice of “Raw Diamonds” that will initially be cut.
The most promising ideas are analyzed and worked on more deeply, taking into account the costs of developing and prototyping these ideas.
This step of the process aims to facilitate the understanding of the requirements necessary to transform an idea into a product or service.
Depending on the result of the analysis of the concepts and functionalities contemplated in the prototype, a Promising Idea can be abandoned or its development postponed. In this phase, the stock of ideas that will pass to the next step will be limited by the budgetary and financial criteria defined initially.
EXPERIMENTATION
4 This is a phase of qualitative research where each idea is transformed into a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to be submitted to market assessment. At the beginning of this phase, the test hypotheses and metrics that will be used for the development of the MVP are established, at the same time that the criteria to be tested are formulated, the expectations of return and the target audience that the product or service reaches.
Read more...4 This is a phase of qualitative research where each idea is transformed into a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to be submitted to market assessment. At the beginning of this phase, the test hypotheses and metrics that will be used for the development of the MVP are established, at the same time that the criteria to be tested are formulated, the expectations of return and the target audience that the product or service reaches.
In other words, here the Promising Idea is transformed into a simplified version of a product or service so that market tests can be made that allow: (a) to know in practice the reaction of the target audience, (b) to understand how audience perceives the product offered and (c) assessing whether the product effectively meets any need or whether it is just the result of a “utopian expectation”, without any correlation with the practical demands of the market.
This exchange of information with the external environment will make it possible to create a reliable way to launch products and services that are, in fact, innovative and feasible from the point of view of financial return.
In this step, a maximum of two or three ideas will be evaluated simultaneously in each Innovation Cycle.


RESULTS ANALYSIS
5 The market information received in the Experimentation step serves as a basis for improvements and adjustments in the concepts and functionalities of the product, at the same time that it allows to create projections and estimates of the project's success, ensuring that the decisions that have to be made they are done supported by effectively reasonable scenarios. This stage is basically based on two studies: Technological Complexity Analysis and Financial Prospective Analysis.
Read more...5 The market information received in the Experimentation step serves as a basis for improvements and adjustments in the concepts and functionalities of the product, at the same time that it allows to create projections and estimates of the project's success, ensuring that the decisions that have to be made they are done supported by effectively reasonable scenarios. This stage is basically based on two studies: Technological Complexity Analysis and Financial Prospective Analysis.
The Technological Complexity Analysis consists of mapping and studying the extent and complexity of the necessary adjustments so that the product or service effectively meets the demand of the target audience.
The Financial Prospective Analysis consists of an in-depth technical study that seeks to create projections and estimates of the economic and financial success of the proposed product or service, based on the market reaction perceived in the Experimentation step. This study will provide Investor Partners with the necessary information to be able to effectively deal with the allocation of project resources or direct these resources to another project.
The completeness, precision and refinement with which these analyzes are conducted are closely linked to each specific situation and to the degree of importance and investments required for the project under analysis.
Projects that are not approved at this step are abandoned or sold to other entrepreneurs, thus allowing the efficient allocation of resources from Investing Partners to more promising projects.
BUSINESS DESIGN
6 In this step, the business chain is perfectly delineated in all its aspects, generating a new Business System to support the evolution of the product or service.
The Business Planning resulting from this phase must define the fundraising strategy, forecast scenarios, define business goals and objectives and plan the growth journey of the new Business System.